Satellite Uplink And Downlink Frequency Range
Iridium satellite frequency description.
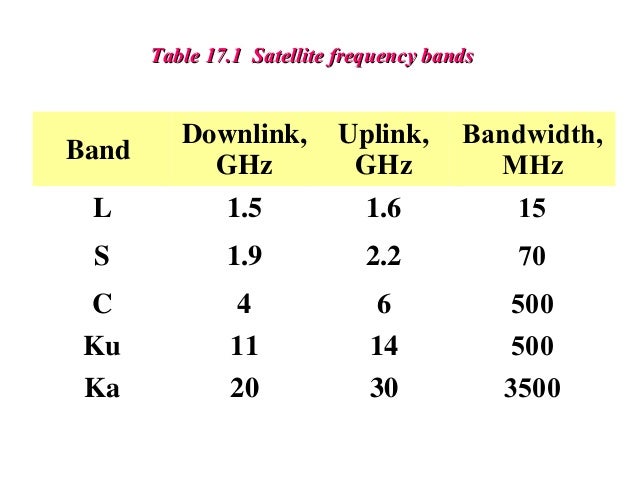
Satellite uplink and downlink frequency range. The downlink chain is built using nearly the same equipment in reverse order. Ka band 26 40 ghz communications satellites uplink in either the 27 5 ghz and 31 ghz bands and high resolution close range targeting radars on military aircraft. For real time updates about which mode the satellite is in see the amsat live oscar satellite status page. Io 86 lapan a2 uplink fm 88 5 hz ctcss downlink fm.
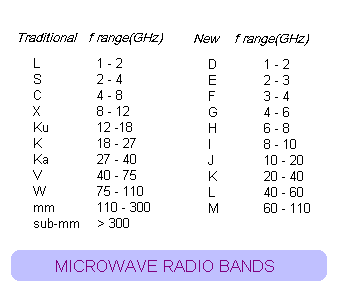
The description provided here is imprecise as the exact configuration can vary widely. There are a number of radio frequency ranges in use in satellite communications such as c x ku ka and even ehg and v band. In some countries the gsm 900 band has been extended to cover a larger frequency range. Take a look at the drawing below and note the path of devices on the left hand.
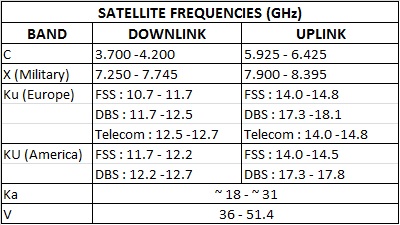
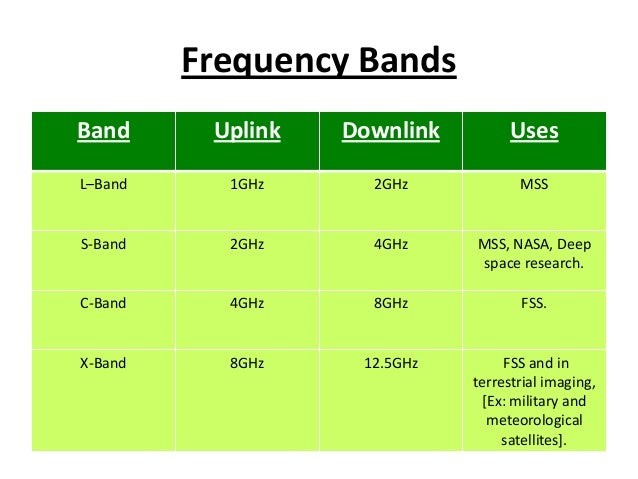
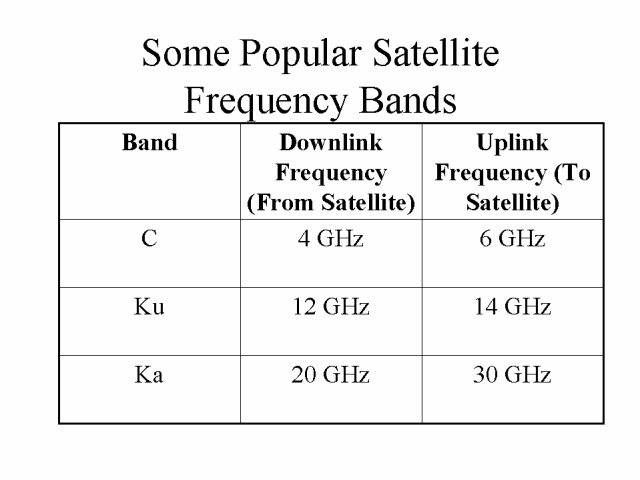
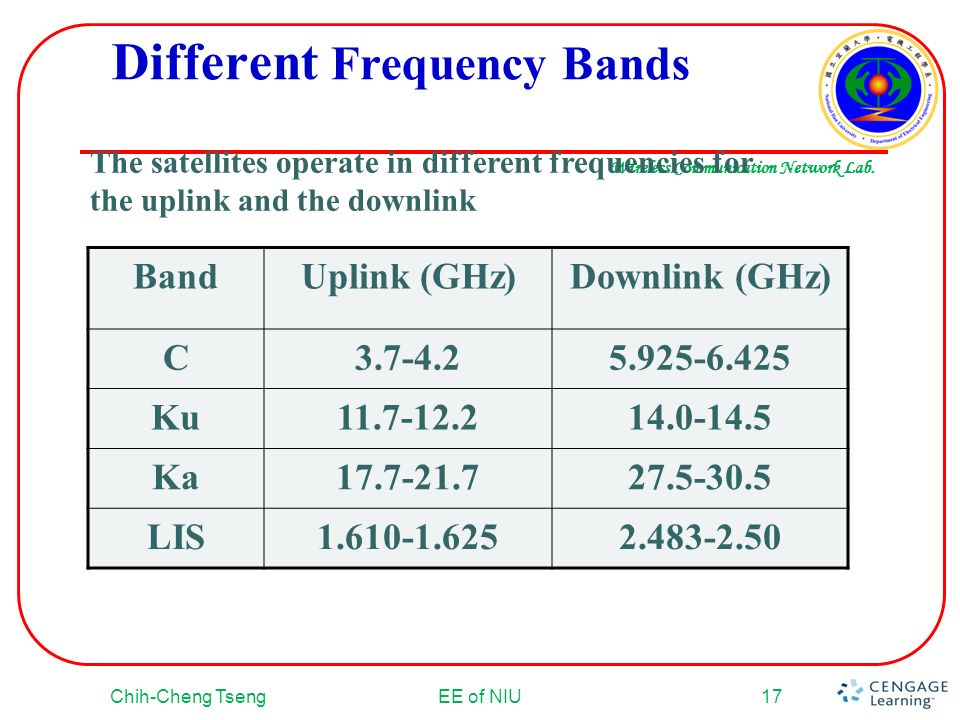
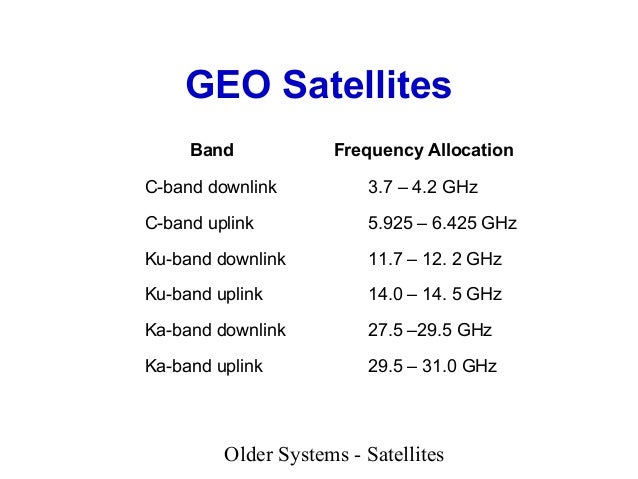
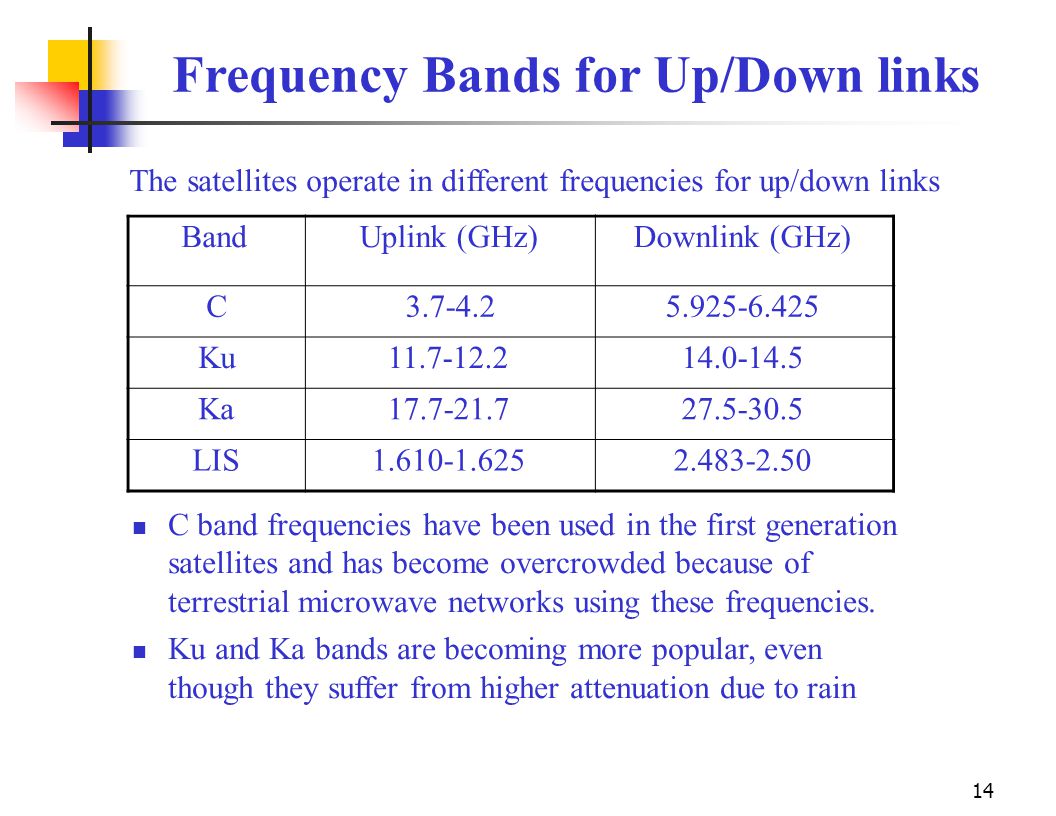
5925 mhz to 6425 mhz is uplink band where as 3700 to 4200 mhz is downlink band. 23 18 to 23 38 ghz. This extended gsm e gsm uses frequency range 880 915 mhz uplink and 925 960 mhz downlink adding 50 channels channel numbers 975 to 1023 and 0 to the original gsm 900 band. The term uplink chain is used to refer to the series of pieces of equipment that are used to produce a radio frequency signal for sending out data.
Because of its weaker power it requires a larger antenna usually above 1 8m 6ft. Simplified summary of ka band satellite allocations annex 1 simplified summary of ka band satellite frequency allocations for communication satellite networks uplink downlink 27 0 ghz 17 3 ghz fss uplink in in regions 1 and 3 band 17 3 18 1 ghz. Duplex spacing of 45 mhz is used. The c band is primarily used for voice and data communications as well as backhauling.
Between iridium phone terminal and iridium satellite. However due to the lower frequency range it performs better under adverse weather conditions on the ground. Between two iridium satellites. Satellite is in a low inclination low earth orbit and not visible north of about 30 degrees north or south of 30.
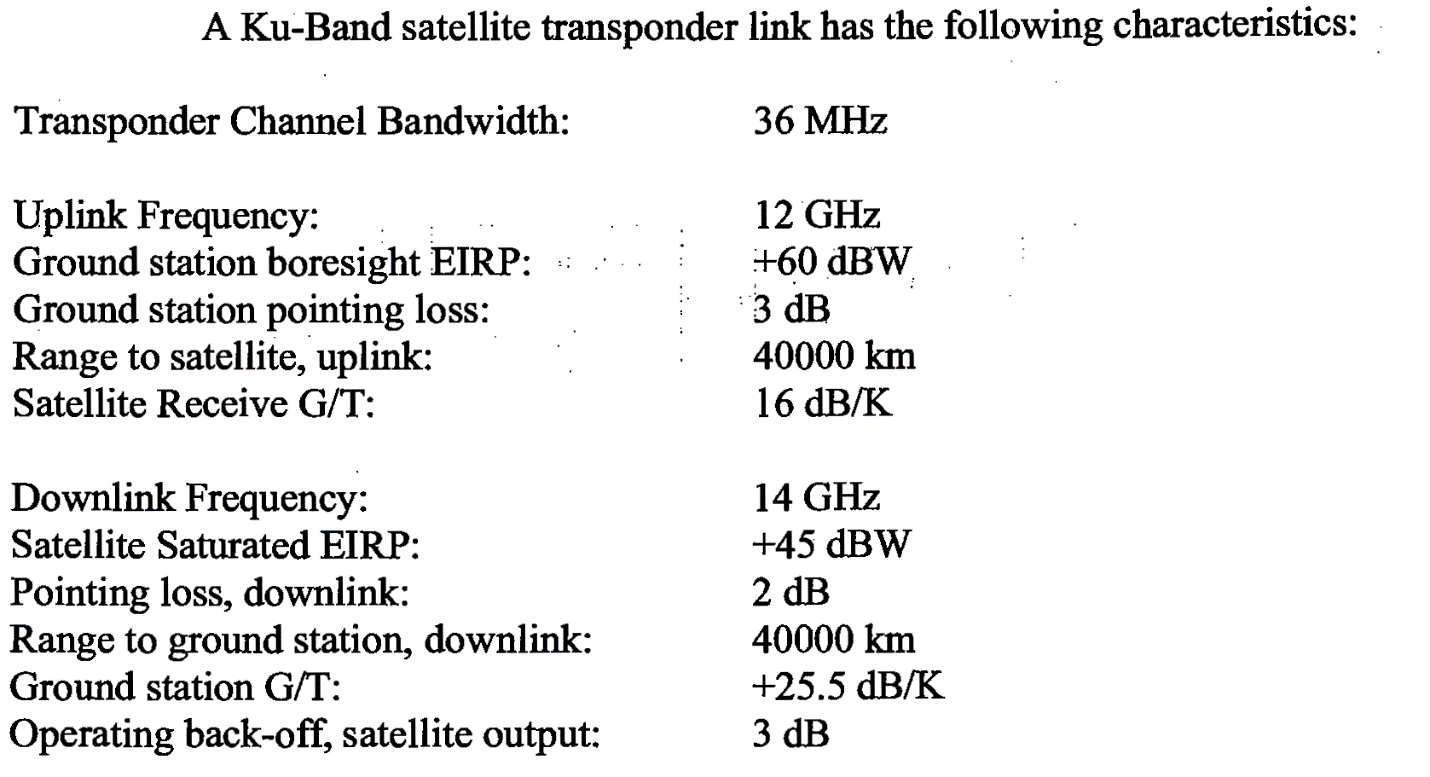
The direction from vsats to sallite is known as uplink and the direction from satellite to vsats is known as downlink. Now as would have thought separate frequency bands are always allocated for uplink and downlink signals often separated by a gap maybe for future allocation since the span of guard bands. To prevent interferance caused by multiple sites transmitting on the same frequencies government agencies and standards organizations around the globe try to keep the usage organized and often such controls take the form of government regulations which carry the weight. In europe ku band downlink is used from 10 7 ghz to 12 75 ghz for direct broadcast satellite services such as astra.